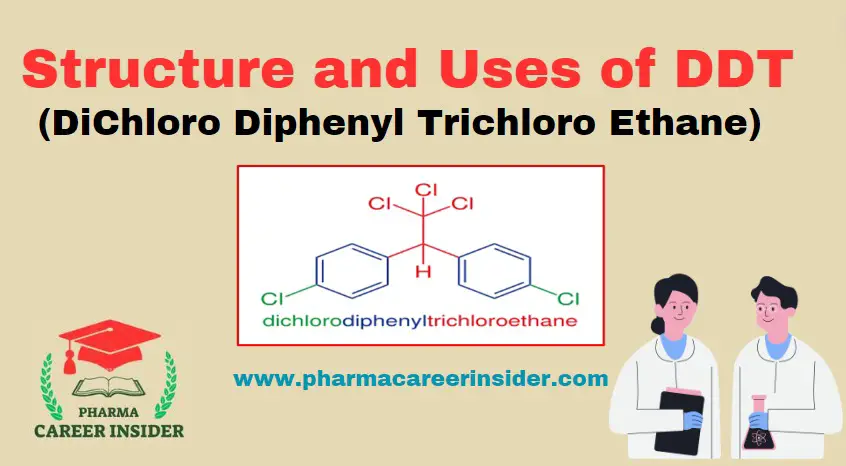
DDT, or Dichloro Diphenyl Trichloroethane, has a molecular formula of C14H9Cl5. The structure of DDT can be represented as follows:
Structure:
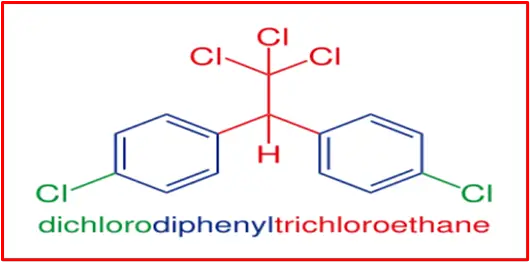
The IUPAC name of DDT is 1,1′-(2,2,2-trichloroethane-1,1-diyl)bis(4-chlorobenzene). Its molecular formula is C14H9Cl5.
Properties:
DDT is a crystalline chemical compound which is colourless, tasteless, hydrophobic, odourless, and low water-soluble but shows good solubility in organic solvents, fats, and oils. It does not occur naturally.
Uses of DDT:
1. Insecticide:
– DDT gained fame as a highly effective insecticide, particularly against mosquitoes that transmit malaria, lice, and other disease-carrying insects.
– It played a crucial role in controlling malaria, contributing to the prevention of millions of deaths.
2. Agricultural Pest Control:
– DDT was extensively used in agriculture to control pests on crops, protect yields, and improve agricultural productivity.
3. Public Health:
– Used for vector control in public health programs, especially in regions with prevalent vector-borne diseases.
4. Livestock Protection:
– DDT protects livestock from insect pests, enhancing animal health.
5. Textile Industry:
– DDT was used in the textile industry to control insects that could damage fabrics.
6. Wood Preservation:
– Applied as a wood preservative to protect against wood-destroying insects.
7. Tsetse Fly Control:
– Used in some regions for controlling tsetse flies, which transmit sleeping sickness.