The Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR) of penicillin reveals key insights into how modifications in its chemical structure affect its pharmacological properties. From variations in the 6-acyl side chain to the substitution patterns on the α-carbon and modifications of the thiazolidine ring, each alteration can significantly impact the antimicrobial activity, stability, and resistance profile of penicillin derivatives.
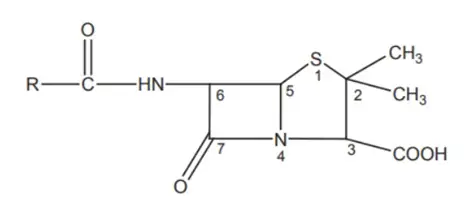
1. 6-Acyl Side Chain:
- Substitution of R on the primary amine with an electron-withdrawing group decreases electron density and protects from acid degradation.
- Substituents on the α-carbon, like amino, chloro, and guanidine, resist acid inactivation.
- Benzylpenicillin is susceptible to acid and alkali degradation and known β-lactamases.
- Varying the acyl amino side chain results in superior biological activity.
- Substitution of α-aryl increases stability and oral absorption.
2. Bulky Groups on α-Carbon:
- Confers β-lactamase resistance.
- Examples: methicillin, nafcillin, oxacillin.
- Attachment of an aromatic ring directly to the side chain amide carbonyl, with substitution at ortho positions, is crucial.
- Size of the aromatic ring system affects penicillinase resistance.
3. Isomeric Forms:
- D-isomer is 2–8 times more active than L-isomer of amoxicillin.
- Introduction of polar or ionized groups into the α-position of the side chain confers activity against gram-negative bacilli.
- Amino, hydroxyl, carboxyl, and sulfonyl groups increase gram-negative activity.
- Examples: ampicillin and carbenicillin.
4. Replacement of Acyl Side Chain:
- Substituting acyl side chain with hydroxymethyl groups improves gram-negative activity.
- Introduction of C-6 α-methoxy group increases stability against β-lactamase.
- N-acylated ampicillins (ureidopenicillins) show increased activity against Pseudomonas.
5. Ester Derivatives:
- Esterification of carboxyl group at C-3 enhances lipophilicity and acid stability.
- Examples: Acetoxymethyl ester derivatives used as prodrugs.
6. Thiazolidine Ring Modifications:
- Replacing sulphur with O, CH, and CH-β-CH3 provides broad-spectrum antibacterial activity.
- Geminal dimethyl group at the C-2 position is characteristic.
- Doubly activated penicillin esters rapidly cleavage in vivo to generate active penicillin.
- Examples: pivampicillin, bacampicillin.
7. In Vitro Degradation:
- pH between 6.0 and 8.0 retards in vitro degradation.
- More lipophilic side chains increase plasma protein binding.
- Examples: Ampicillin (25% plasma protein bound), phenoxy methyl penicillin (75% plasma protein bound).