Introduction
The rotating platinum electrode (RPE) is a working electrode used in electrochemical analysis, particularly in voltammetry and polarography. Unlike the dropping mercury electrode (DME), the RPE consists of a solid platinum disk that rotates at a controlled speed within the solution. The rotation enhances mass transport, ensuring a uniform distribution of the analyte near the electrode surface.
This electrode is commonly used for studying reaction kinetics, diffusion-controlled processes, and electrodeposition due to its ability to provide a stable and well-defined current response.
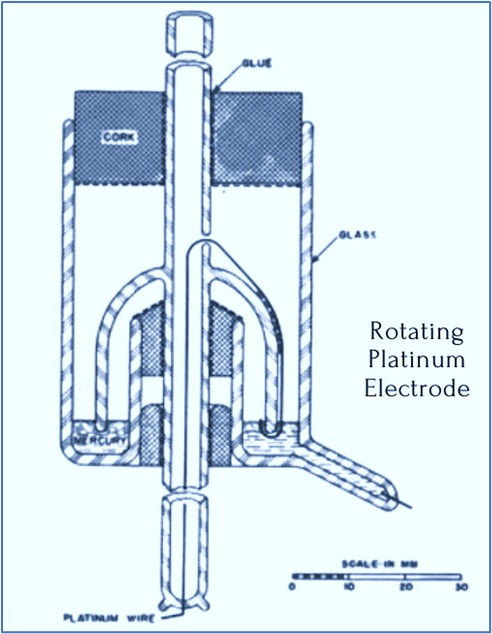
Construction of RPE
The rotating platinum electrode consists of the following key components:
- Platinum Disk: Acts as the working electrode, where electrochemical reactions occur.
- Rotating Shaft: Connects the electrode to a motor that controls the rotation speed.
- Motor & Control System: Allows precise adjustment of the rotation speed to control the mass transport of the analyte.
- Reference & Counter Electrodes: Used to complete the electrochemical circuit, often a saturated calomel electrode (SCE) or a silver/silver chloride (Ag/AgCl) electrode.
Working Principles of RPE
- The platinum disk electrode rotates at a controlled speed, creating a convective flow in the solution.
- This rotation enhances mass transfer, reducing concentration polarization and ensuring a steady-state current.
- The applied potential causes the electroactive species in the solution to undergo oxidation or reduction at the electrode surface.
- The current response is recorded, and a voltammogram (graph of current vs. potential) is obtained.
- The mass transfer rate depends on the rotation speed (ω), following the Levich equation, which describes the relationship between current and rotation speed.
Advantages
- Enhanced Mass Transport: The rotation ensures a constant supply of reactants to the electrode, improving sensitivity.
- Stable Current Response: Unlike DME, which has a fluctuating surface, RPE provides a steady-state signal.
- Versatility: Can be used for both oxidation and reduction reactions.
- Reproducibility: Provides a consistent reaction environment, reducing experimental variability.
Disadvantages
- Expensive & Complex Setup: Requires a precise motor-controlled system for rotation.
- Prone to Fouling: The solid platinum surface can be contaminated over time, requiring frequent cleaning.
- Limited Surface Renewal: Unlike DME, the electrode surface does not regenerate automatically, making maintenance essential.
Applications
- Electrochemical Kinetics: Used to study reaction rates and diffusion processes.
- Electrocatalysis: Helps in understanding catalytic mechanisms, particularly in fuel cells.
- Metal Deposition Studies: Used in electroplating and corrosion analysis.
- Sensor Development: Plays a role in developing sensors for detecting trace metals and biomolecules.
Comparison of RPE vs. DME

Conclusion
The Rotating Platinum Electrode (RPE) is a powerful tool in electrochemical analysis, offering enhanced mass transport, stable current response, and versatility for both oxidation and reduction reactions. However, it requires careful maintenance and a controlled rotation system. While it is a preferred choice in kinetic studies and electrocatalysis, the Dropping Mercury Electrode (DME) remains advantageous for reduction-based analyses due to its self-renewing surface.