Diphenylmethane, chemically represented as (C6H5)2CH2 or (CH2Ph2), is an organic compound comprising a methane molecule with two hydrogen atoms substituted by two phenyl groups. It exists as a white solid at room temperature.
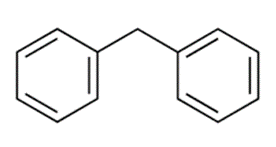
Method of preparation of Diphenylmethane:
The diphenylmethane can be prepared through several methods, this is including as-
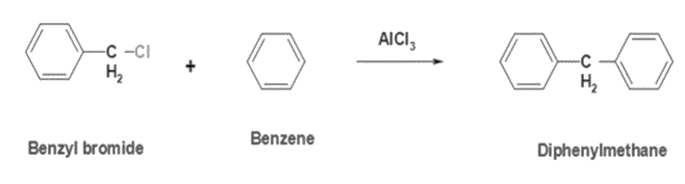
1. Friedel-Crafts Reaction: This method involves the reaction of benzene with benzyl chloride in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst such as aluminium chloride (AlCl3). The reaction proceeds via electrophilic aromatic substitution to yield diphenylmethane.
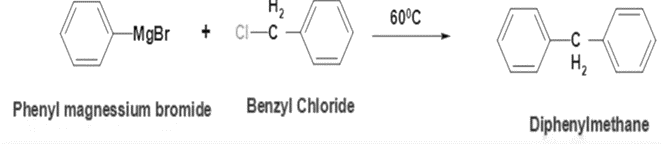
2. Grignard Reaction: To form diphenylmethane, benzyl chloride can react with a Grignard reagent such as phenyl magnesium bromide (PhMgBr) or phenyl lithium (PhLi). This reaction proceeds via nucleophilic addition of the Grignard reagent to the benzyl chloride.
3. Wurtz Reaction: In this method, benzyl chloride is treated with sodium metal (Na) in a suitable solvent such as dry ether. The sodium metal undergoes a single electron transfer to form a radical, which then couples with another benzyl radical to yield diphenylmethane.
Uses of Diphenylmethane:
Diphenylmethane has several uses in various industries:
Polymer Chemistry: It is a crucial component in producing polyurethane foams and resins, and it is widely used in insulation, construction, automotive, and furniture industries.
Fragrance Industry: Diphenylmethane derivatives are utilized as fragrances and flavoring agents in perfumes, cosmetics, and food products, enhancing their sensory appeal.
Chemical Synthesis: It acts as an intermediate in organic synthesis, enabling the production of pharmaceuticals, fragrances, dyes, and other complex molecules.
Solvent: Diphenylmethane is a solvent in various chemical processes and industrial applications due to its good solubility for organic and inorganic substances.
Pharmaceuticals: It serves as a building block for synthesizing drugs, including antihistamines, analgesics, and anti-inflammatory agents, contributing to the pharmaceutical industry.
Conclusion:
Discover the versatility of Diphenylmethane, an organic compound renowned for its myriad applications. Learn about its chemical structure and methods of preparation, including Friedel-Crafts Reaction and Grignard Reaction. Explore its diverse uses across industries, from polymer chemistry and fragrance production to pharmaceuticals and beyond.




