What is the Nipah Virus?
The Nipah virus (NiV) is a highly dangerous zoonotic virus that can spread from animals to humans and also between humans. In recent years, Nipah virus outbreaks have raised serious global health concerns due to their high fatality rate, lack of a specific cure, and potential to cause severe neurological and respiratory illness.
In 2026, the Nipah virus once again captured global attention as new suspected and confirmed cases were reported in parts of India, triggering widespread searches and public concern. Health authorities worldwide are closely monitoring the situation because the Nipah virus is listed by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a priority pathogen with epidemic potential. This comprehensive guide explains everything you need to know about the Nipah virus, from its origin and symptoms to treatment, prevention, and the latest updates, using medically accurate yet easy-to-understand language.
History of Nipah Virus Outbreaks
The Nipah virus was first identified during an outbreak in Malaysia and Singapore between 1998 and 1999. The outbreak primarily affected pig farmers and slaughterhouse workers. The virus was traced back to fruit bats, which infected pigs, and the pigs then transmitted the virus to humans. More than 100 people died, and over a million pigs were culled to control the outbreak. This event revealed the virus’s ability to jump between species and cause deadly human disease.
Major Nipah Virus Outbreaks by Country
Since its discovery, Nipah virus outbreaks have been reported in several countries:
- Bangladesh: Frequent outbreaks, often linked to consumption of raw date palm sap contaminated by bats
- India: Multiple outbreaks, especially in Kerala and eastern regions
- Malaysia & Singapore: Early outbreaks linked to pig farming
- Other regions: Serological evidence in parts of Southeast Asia
Each outbreak has reinforced the virus’s reputation as one of the most lethal emerging infectious diseases.
Nipah Virus in 2026 – Latest Global & India Updates
Why the Nipah Virus is in the News Now
In 2026, the Nipah virus became a trending global topic due to:
- Reports of suspected and confirmed cases
- Rapid rise in Google search trends
- Alerts issued by health departments and hospitals
- Increased surveillance by global health agencies
Unlike many viral infections, even a small cluster of Nipah cases can trigger emergency responses because of its high mortality rate and outbreak potential.
Nipah Virus Situation in India
India has experienced multiple Nipah virus outbreaks in the past, particularly in West Bengal and Kerala, where quick containment efforts prevented large-scale spread. In 2026, new alerts and suspected cases in eastern India, including West Bengal, have led to heightened surveillance.
Indian health authorities have implemented:
- Rapid contact tracing
- Isolation protocols
- Testing and monitoring of high-risk contacts
- Public awareness campaigns
So far, officials emphasize that panic is not required, but vigilance is essential.
What Causes Nipah Virus Infection?
Nipah virus belongs to the Paramyxoviridae family and the Henipavirus genus. It is a single-stranded RNA virus capable of infecting both animals and humans.
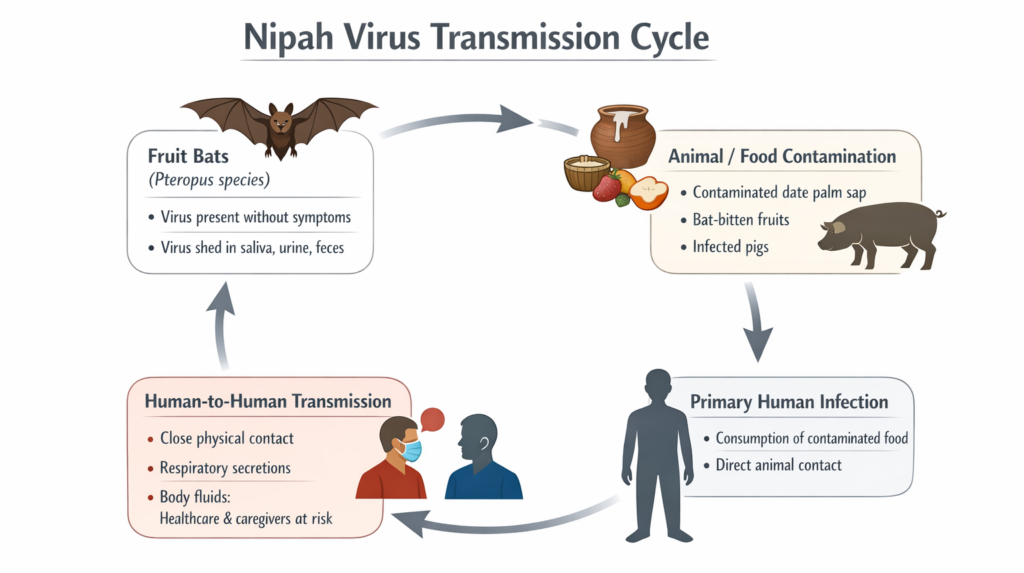
Natural Reservoir
The natural hosts of the Nipah virus are fruit bats, particularly bats of the Pteropus genus. These bats carry the virus without showing symptoms and can shed it through saliva, urine, and feces.
Humans become infected either directly from bats or indirectly through other animals or contaminated food.
How Does Nipah Virus Spread? (Transmission)
- Animal-to-Human Transmission: Nipah virus can spread to humans through:
- Consumption of raw date palm sap contaminated by bat saliva or urine
- Eating fallen or bitten fruits
- Close contact with infected animals, such as pigs
This form of transmission has been responsible for many early outbreaks.
2. Human-to-Human Transmission: Human-to-human transmission occurs through:
- Close physical contact
- Exposure to respiratory secretions
- Contact with bodily fluids of infected individuals
Healthcare workers and family caregivers are at higher risk without proper protective measures.
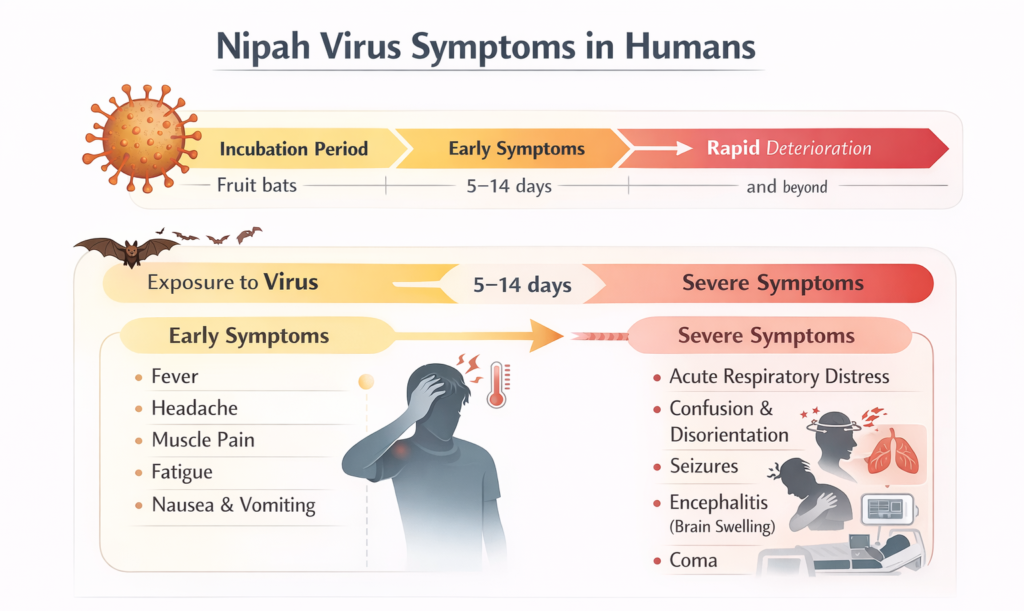
Nipah Virus Symptoms in Humans
Symptoms of Nipah virus infection can range from mild to severe and may appear 5 to 14 days after exposure.
1. Early Symptoms: Common early symptoms include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle pain
- Fatigue
- Nausea and vomiting
These symptoms often resemble common viral infections, making early diagnosis difficult.
2. Severe Symptoms: As the disease progresses, patients may develop:
- Acute respiratory distress
- Confusion and disorientation
- Seizures
- Encephalitis (brain inflammation)
- Coma
Severe cases can deteriorate rapidly, sometimes within days.
Nipah Virus Fatality Rate & Risk Factors
One of the most alarming aspects of the Nipah virus is its high fatality rate, which ranges from 40% to 75%, depending on the outbreak and quality of medical care. Risk Factors Include:
- Close contact with infected persons
- Consumption of contaminated food
- Healthcare exposure without protection
- Pre-existing medical conditions
Because of its lethality, the Nipah virus is considered a serious global health threat.
How is Nipah Virus Diagnosed?
Early diagnosis is critical but challenging. Diagnostic Methods Include:
- RT-PCR tests to detect viral RNA
- Blood tests
- Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis
- Serological tests for antibodies
Samples must be handled in high-security laboratories due to the virus’s dangerous nature.
Nipah Virus Treatment Options
Is There a Cure for Nipah Virus?
Currently, there is no specific antiviral drug approved to treat Nipah virus infection.
Supportive Treatment Includes:
- Intensive care unit (ICU) support
- Mechanical ventilation for respiratory failure
- Management of brain swelling
- Treatment of secondary infections
Some experimental treatments and monoclonal antibodies are under investigation, but none are widely available yet.
Is There a Vaccine for Nipah Virus?
As of 2026, no licensed vaccine is available for the Nipah virus.
However:
- Several vaccine candidates are under development
- WHO has classified the Nipah virus as a priority disease
- Global research efforts are ongoing
A successful vaccine could significantly reduce future outbreak risks.
Prevention & Safety Measures
How to Prevent Nipah Virus Infection
Key preventive measures include:
- Avoid eating fallen or partially eaten fruits
- Do not consume raw date palm sap
- Wash fruits thoroughly before consumption
- Maintain proper hand hygiene
Hospital & Community Prevention
Healthcare facilities should ensure:
- Use of personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Isolation of suspected cases
- Strict infection control protocols
Public education plays a vital role in prevention.
Nipah Virus vs COVID-19
Although both are viral diseases, the Nipah virus and COVID-19 differ significantly.
| Feature | Nipah Virus | COVID-19 |
| Transmission | Limited human-to-human | Highly contagious |
| Fatality Rate | Very high | Relatively lower |
| Vaccine | Not available | Widely available |
| Spread | Localized outbreaks | Global pandemic |
Nipah virus does not spread as easily as COVID-19, but it is far more deadly.
WHO & Global Health Response
The World Health Organization (WHO) actively monitors Nipah virus outbreaks and supports countries with:
- Surveillance systems
- Emergency preparedness
- Research coordination
- Public health guidance
International collaboration is essential to prevent Nipah from becoming a larger global crisis.
Conclusion
Nipah virus is one of the most dangerous emerging infectious diseases known to humanity. While it does not spread as rapidly as some viruses, its high fatality rate and lack of a vaccine make it a serious concern. Public awareness, early detection, strong healthcare systems, and global cooperation are the most effective tools we have to prevent future outbreaks. Staying informed and following preventive guidelines can save lives.
Medical Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult healthcare authorities for diagnosis and treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1. Is the Nipah virus present in India now?
Answer: Health authorities report isolated cases and alerts, but there is no widespread outbreak.
Q2. Can the Nipah virus spread like COVID-19?
Answer: No. Nipah virus spreads through close contact and is not as contagious.
Q3. Is the Nipah virus airborne?
Answer: There is no evidence of airborne transmission.
Q5. Can the Nipah virus be cured?
Answer: There is no specific cure, but early supportive care improves survival.
Q6. Should we panic about the Nipah virus?
Answer: No. Awareness and prevention are more important than panic.
Q7. Is there a Nipah virus outbreak in India?
Answer: As of now, India has reported isolated cases and alerts related to the Nipah virus, mainly in high-risk regions. There is no nationwide outbreak, but health authorities are maintaining strict surveillance to prevent spread.
Q8. Is the Nipah virus deadly?
Answer: Yes, the Nipah virus is considered highly dangerous because it has a high fatality rate ranging from 40% to 75% in reported outbreaks. However, early detection, isolation, and proper supportive medical care can improve survival.
Q9. How many people died in Kerala due to Nipah virus?
Answer: Kerala has experienced multiple Nipah virus outbreaks since 2018. Across different outbreaks, several deaths have been reported, but quick public health response helped prevent large-scale spread. Exact numbers vary by outbreak and official health reports.
Q10. How to stay safe from the Nipah virus?
Answer: To reduce the risk of Nipah virus infection: Follow guidelines issued by health authorities
- Avoid eating fallen or bat-bitten fruits
- Do not consume raw date palm sap
- Wash fruits thoroughly before eating
- Maintain proper hand hygiene
- Avoid close contact with infected persons




