Normality (N) is an important unit of concentration used in chemistry, pharmacy, and research. It measures the number of equivalents of solute per liter of solution. This tool allows you to calculate normality instantly online by entering weight, equivalent weight, and solution volume.
Normality Calculator
Normality Calculator
Formula: Normality (N) = (Weight of Solute (g)) / (Equivalent Weight (g/equiv) × Volume of Solution (L))
Inputs
Results
Calculated Value:
Formula with Values:
Interpretation:
How to Use This Calculator?
Enter the weight of solute in grams.
Enter the equivalent weight (for acids, bases, or salts).
Enter the volume of solution in liters.
Click Calculate to get normality along with the formula and interpretation.
What is normality (N)?
Normality is a measure of concentration expressed as the number of gram equivalents of solute per liter of solution. It is especially useful in acid-base titrations, redox reactions, and stoichiometry because it considers the valency factor (n-factor) of reactants.
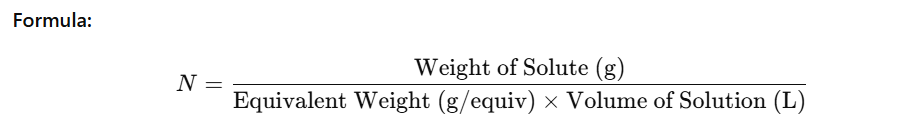
Example Calculation
Suppose you dissolve 5 g of H₂SO₄ (sulfuric acid) in 250 L of solution. Equivalent weight of H₂SO₄ = 49.04 g/equiv.
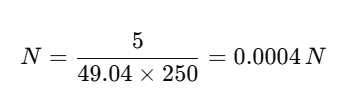
This means the solution contains 0.0004 equivalents of H⁺ per liter.
Conclusion
This Normality Calculator (2025) is a quick and reliable way to calculate the concentration of solutions in terms of equivalents. It is useful for chemistry students, pharmacy professionals, and researchers working with acid-base titrations, redox reactions, and analytical chemistry.
👉 Try it above and save time in your lab calculations!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Q1. What is Normality (N)?
- Normality is the number of equivalents of solute per liter of solution. It is especially useful in acid-base and redox reactions.
Q2. What is the difference between Normality and Molarity?
- Molarity (M): moles of solute per liter (focuses on particles).
- Normality (N): equivalents per liter (focuses on reacting capacity).
👉 Example: 1 M HCl = 1 N, but 1 M H₂SO₄ = 2 N.
Q3. What is Equivalent Weight?
Equivalent weight = molar mass ÷ valency factor.
- HCl = 36.46 ÷ 1 = 36.46 g/equiv
- H₂SO₄ = 98.08 ÷ 2 = 49.04 g/equiv
Q4. Can this calculator be used for redox reactions?
Yes, by using the correct equivalent weight (molar mass ÷ number of electrons transferred).
Q5. How do I convert mL to L for input?
Simply divide mL value by 1000. Example: 250 mL = 0.25 L.





Yes, it’s doing good work.
Thank you for your valuable feedback.
Thanks sir it’s so helpful, I appreciate your effort
Thank you for your valuable feedback.
Very good tool. It reduces calculation time. Very helpful for chemistry aspirants.
Great work punet sir please keep it up for your students.
🙏🏻👍🏻👍🏻
Thank you for your valuable feedback.