Meta Description:
Learn about flocculated suspensions and their definition, characteristics, preparation, advantages, and applications. Understand why they are essential in pharmaceuticals and other industries.
Introduction
Flocculated suspensions are a type of pharmaceutical formulation where insoluble solid particles aggregate into loose clusters, known as flocs, preventing the formation of a hard sediment. These suspensions ensure easy redispersion, making them ideal for pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and industrial applications.
In this article, we will explore the definition, characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, preparation methods, and applications of flocculated suspensions.
Definition of Flocculated Suspensions
A flocculated suspension is a system where small particles form loose networks (flocs) due to weak interparticle forces, such as van der Waals forces or electrostatic attraction. These flocs settle rapidly but do not form a hard cake, ensuring easy redispersion upon shaking.
Characteristics of Flocculated Suspensions
Easy Redispersion: The sediment is loosely packed and can be easily resuspended.
High Sedimentation Rate: Due to floc formation, particles settle quickly but do not form a hard cake.
Distinct Boundaries: The clear separation between the sediment and supernatant is visible.
Lower Viscosity: Compared to deflocculated suspensions, flocculated suspensions have lower viscosity, making them easier to pour and administer.
Comparison: Flocculated vs. Deflocculated Suspensions
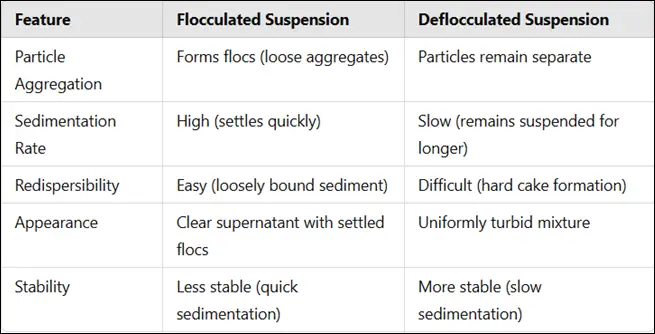
Preparation of Flocculated Suspensions
To prepare a flocculated suspension, flocculating agents are used to promote particle aggregation while preventing hard caking.
Key Components:
- Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API): The insoluble drug particles.
- Flocculating Agents: Substances that encourage floc formation (e.g., electrolytes, surfactants, polymers).
- Dispersing Medium: Usually water or an oil-based liquid.
- Wetting Agents: Agents that reduce surface tension and improve dispersion (e.g., glycerin, polysorbates).
- Suspending Agents: Maintain uniformity and prevent rapid settling (e.g., bentonite, xanthan gum).
Steps to Prepare a Flocculated Suspension:
- Disperse the active drug in the chosen medium with the help of wetting agents.
- Add flocculating agents such as electrolytes (e.g., sodium chloride, potassium chloride) to promote flocculation.
- Incorporate suspending agents to slow down sedimentation and improve stability.
- Adjust pH and viscosity for optimal formulation stability.
- Mix thoroughly and transfer the suspension into a container with proper labeling.
Factors Affecting Stability of Flocculated Suspensions
Several factors influence the stability and effectiveness of flocculated suspensions. Understanding these factors is crucial to optimizing formulation and ensuring long-term usability.
- Particle Size and Distribution: Smaller particles provide better suspension stability but may require stronger flocculating agents. Large, uneven particle sizes can lead to inconsistent sedimentation.
- pH of the Medium: pH can affect the charge on particles, influencing their ability to form flocs. A well-adjusted pH ensures that flocculated particles remain loosely aggregated and redispersible.
- Type and Concentration of Flocculating Agents: Too much flocculating agent can lead to excessive sedimentation. Too little may result in a hard cake (deflocculated suspension).
- Electrolyte Concentration: The presence of salts and electrolytes can alter particle interactions. Optimal electrolyte levels improve suspension stability.
- Viscosity of the Dispersion Medium: Higher viscosity can slow sedimentation but may make redispersion more difficult. Optimal viscosity ensures a balance between suspension stability and ease of use.
- Temperature and Storage Conditions: Temperature fluctuations can cause phase separation and instability. Proper storage conditions (a cool, dry place) enhance the longevity of the suspension.
Advantages of Flocculated Suspensions
- Prevents Hard Caking: Unlike deflocculated suspensions, flocs do not form a compact sediment.
- Easy Redispersion: A simple shake restores uniformity.
- More Uniform Dosing: Ensures even distribution of the drug in each dose.
- Better Patient Compliance: Easier to administer compared to hard-to-redisperse deflocculated suspensions.
Disadvantages of Flocculated Suspensions
- Rapid Sedimentation: Requires frequent shaking before administration.
- Less Physically Stable: Prone to phase separation over time.
- Requires More Excipients: Additional flocculating and suspending agents increase formulation complexity and cost.
Examples of Flocculated Suspensions in Pharmaceuticals
Flocculated suspensions are widely used in various pharmaceutical formulations to enhance drug stability and bioavailability.
1. Antibiotic Suspensions
- Example: Amoxicillin suspension
- Used to deliver antibiotics in liquid form for pediatric and geriatric patients.
2. Antacid Suspensions
- Example: Magnesium hydroxide suspension
- Provides relief from acid reflux and indigestion.
3. Steroid Suspensions
- Example: Prednisolone acetate eye drops
- Used in ophthalmic formulations for anti-inflammatory treatment.
4. Vaccines and Injectable Suspensions
- Example: Insulin suspensions
- Used for controlled release of medications in injectable formulations.
5. Cosmetic and Skincare Suspensions
- Example: Calamine lotion
- Provides relief from skin irritation and rashes.
Applications of Flocculated Suspensions
Flocculated suspensions are widely used in various industries:
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Used in antacid suspensions, antibiotics (e.g., amoxicillin suspensions), and steroid formulations.
- Cosmetic Industry: Found in lotions, creams, and emulsions.
- Food Industry: Used in beverages, sauces, and dressings where solid particles need to remain suspended.
- Chemical Industry: Utilized in paints, coatings, and ceramic suspensions to maintain consistency.
Conclusion
Flocculated suspensions offer a practical solution for formulations where insoluble particles must remain dispersed. Their ease of redispersion makes them superior to deflocculated suspensions, but their rapid sedimentation requires frequent shaking. With proper formulation using flocculating and suspending agents, they provide effective drug delivery, enhanced patient compliance, and stable liquid dosage forms.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a flocculated suspension?
Answer: A flocculated suspension is a system where insoluble particles form loose aggregates (flocs) that settle quickly but are easily redispersed upon shaking.
2. How do you prepare a flocculated suspension?
Answer: Flocculated suspensions are prepared using flocculating agents (e.g., electrolytes, surfactants, polymers) to encourage particle aggregation while preventing hard sedimentation.
3. What is the difference between flocculated and deflocculated suspensions?
Answer: Flocculated suspensions form loose aggregates that settle quickly but are easily redispersed, while deflocculated suspensions have individual particles that settle slowly but may form a hard cake.
4. Why are flocculated suspensions used in pharmaceuticals?
Answer: They ensure uniform dosing and easy administration and prevent hard caking, making them ideal for antibiotics, antacids, and steroid suspensions.
5. What are common flocculating agents?
Answer: Common flocculating agents include electrolytes (e.g., sodium chloride), polymers (e.g., gelatin), and surfactants (e.g., polysorbates).




